Surgery: Difference between revisions
(Multisurgery is kill) |
m (Mentioned damage breaking bones) |
||
| Line 100: | Line 100: | ||
# (Optional) Complete [[Surgery#Prepping_for_Surgery|Prepping for Surgery]]. | # (Optional) Complete [[Surgery#Prepping_for_Surgery|Prepping for Surgery]]. | ||
# Perform '''Opening a Surgical Site'''. | # Perform '''Opening a Surgical Site'''. | ||
# Ensure the target limb doesn't have any damage, otherwise the bone will break again. | |||
# Apply [[File:Bone gel.png]] '''bone gel''' to the broken bone. | # Apply [[File:Bone gel.png]] '''bone gel''' to the broken bone. | ||
# Use the [[File:Bone setter.png]] '''bone setter''' to put the bone in place. | # Use the [[File:Bone setter.png]] '''bone setter''' to put the bone in place. | ||
Revision as of 13:45, 25 January 2018
A Guide to Surgery In General
All surgery requires the set of medical tools in the Operating Theatre, along with an operating table. Ideally, only Surgeons and the Chief Medical Officer can perform advanced surgery. Remember to let each step complete fully, else you risk harming yourself or your patient like playing dangerously and want to ace that surgery.
Ghetto Surgery
Don't. It's not worth it. No one wants to see blood, guts, and a sweaty physician trying to extract an appendix from someone on the bar table.
Surgical Tools
Surgery tools aren't common and are pretty much only found in the operating rooms.
The following are the standard surgical tools most doctors will need:
Infection
Place on gloves and wash your hands before every surgery. Failure to do so will result in giving your patient an infection which, if left untreated, can be deadly. Apply ointment to the afflicted areas quickly if you fail to wash your hands before starting surgery. Make sure to clean your tools after every surgery as well with a spray bottle of either space cleaner or sterilizine
Prepping for Surgery
Please ensure that your patients are properly diagnosed and scanned in a body scanner before starting the operation, and that all medications and personnel needed for the procedure have been prepared.
- Find a suitable
 operating table.
operating table. - Make sure you're wearing
 latex gloves and a
latex gloves and a  sterile mask.
sterile mask. - Ask the person to strip, or clickdrag them onto your body and click on all of their items to remove them.
 Grab the person and click on the operating table to lay them down on it.
Grab the person and click on the operating table to lay them down on it.- Check the
 Operating Computer to ensure the patient is positioned properly; if the monitor does not show the patient's vitals, the surgery will not work.
Operating Computer to ensure the patient is positioned properly; if the monitor does not show the patient's vitals, the surgery will not work. - Pick up a
 medical mask and
medical mask and  sleeping agent.
sleeping agent. - Clickdrag their body onto yours to view their inventory. Place the medical mask on their mask slot and the tank of nitrous on their back.
- Clickdrag their body onto yours once again to refresh the window. A new option called Set Internals will appear towards to bottom. Clicking it will turn on the anesthetics after a short while.
- Examine the patient until it reports that they are unconscious.
- Make sure you're set on the
 Help intent.
Help intent. - Use a sink to wash your hands. Unclean hands can result in an infected wound. This is treatable with ointment.
NOTE: If anyone is pulling on the patient, the surgery will not work properly! Make sure no one is pulling the patient!
Surgery List
There are many different types of surgeries that can be performed. Sometimes it will be necessary to have the patient hooked up to an IV or someone on standby to inject medications during the procedure.
Opening a Surgical Site
The first steps of most surgeries.
- NOTE: Steps 3-5 can be replaced with one use of an
 IMS if one is available to you.
IMS if one is available to you.
- (Optional) Complete Prepping for Surgery.
- Aim for the location in the
 Damage Zone.
Damage Zone. - Use the
 scalpel to create an incision.
scalpel to create an incision. - Use the
 hemostat to stop any potential bleeding.
hemostat to stop any potential bleeding. - Use your
 retractors to lift up the skin.
retractors to lift up the skin.
For internal work in chest and skull only:
Closing a Surgical Site
The final steps of most surgeries.
If you had to use the ![]() bone saw earlier (chest/head):
bone saw earlier (chest/head):
- Use your
 retractors to put the bones back into place.
retractors to put the bones back into place. - Apply
 bone gel to mend their ribcage/skull unless the bone was fractured during the sawing phase, in which case, conduct bone repair before continuing.
bone gel to mend their ribcage/skull unless the bone was fractured during the sawing phase, in which case, conduct bone repair before continuing.
Then after the above (or if it was not required):
Bone Repair
The mending of broken bones and fractures.
- NOTE: Steps 3-5 can be replaced with one use of a
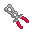 Boneclamp if one is available to you.
Boneclamp if one is available to you.
- (Optional) Complete Prepping for Surgery.
- Perform Opening a Surgical Site.
- Ensure the target limb doesn't have any damage, otherwise the bone will break again.
- Apply
 bone gel to the broken bone.
bone gel to the broken bone. - Use the
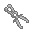 bone setter to put the bone in place.
bone setter to put the bone in place. - Apply more
 bone gel.
bone gel. - Perform Closing a Surgical Site.
Facial Reconstruction
The fixing of facial and vocal deformaties.
- (Optional) Complete Prepping for Surgery.
- Aim for the patient's mouth - not head - in the
 Damage Zone.
Damage Zone. - Cut the skin with your
 scalpel.
scalpel. - Use your
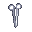 hemostat to mend their vocal cords.
hemostat to mend their vocal cords. - Use your
 retractors to put the skin back in place.
retractors to put the skin back in place. - Cauterize the wound with the
 cautery.
cautery.
Internal Bleeding
Repairing damaged arteries and veins within the body to stop internal bleeding.
- (Optional) Complete Prepping for Surgery.
- Perform the steps in Opening a Surgical Site.
- Use the
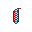 FixOVein to repair the damaged blood vessels.
FixOVein to repair the damaged blood vessels. - Perform the steps in Closing a Surgical Site.
Appendectomy
Removal of an inflamed appendix.
- (Optional) Complete Prepping for Surgery.
- Aim for the patient's groin in the
 Damage Zone.
Damage Zone. - Perform the steps in Opening a Surgical Site.
- Use your
 scalpel to cut out the appendix.
scalpel to cut out the appendix. - Use your
 hemostat to extract the appendix.
hemostat to extract the appendix. - (Optional) Dispose of the newly extracted appendix.
- Perform the steps in Closing a Surgical Site.
Limb Replacement
Replacing missing limbs with new ones.
- (Optional) Complete Prepping for Surgery.
- Aim for the patient's affected (missing) limb using the
 Damage Zone.
Damage Zone. - Attach the appropriate limb, either mechanical or organic.
- Use the
 hemostat if the limb is organic to reattach tendons and muscles.
hemostat if the limb is organic to reattach tendons and muscles. - Use a
 trauma kit if the patient requires one (may need to be applied to either the new limb, or the 'parent' body part it was attached to).
trauma kit if the patient requires one (may need to be applied to either the new limb, or the 'parent' body part it was attached to). - Ensure the patient is able to manipulate their new limb before releasing them.
Internal Organs Osteopathy
Mending damaged organs such as lungs, liver, and brain.
- (Optional) Complete Prepping for Surgery.
- Aim for the chest, groin, or head in the
 Damage Zone.
Damage Zone. - Perform the steps in Opening a Surgical Site.
- Use the appropriate mechanism to mend the organ:
- Perform the steps in Closing a Surgical Site.
Cavity Surgery
Putting things inside peoples' body cavities, such as NIFs.
Maxiumum size of item that fits inside:
- Head - tiny (i.e. pen, paper, NIF)
- Abdomen - pocket-size (i.e. most surgical tools)
- Chest - small (i.e. bone saw, revolver)
- Aim for the chest, abdomen or head in the
 Damage Zone.
Damage Zone. - Perform the steps in Opening a Surgical Site.
- Use the
 surgical drill to prepeare cavity.
surgical drill to prepeare cavity. - Insert the item inside. If it caused internal bleeding, use FixOVein to fix it.
- If you decided not to put item inside, use
 cautery to mend cavity wall.
cautery to mend cavity wall. - Perform the steps in Closing a Surgical Site.
Implant/Shrapnel Removal
Removing implants from the body. Also removeal of things from body cavities.
- (Optional) Complete Prepping for Surgery.
- Aim for the implant location on the
 Damage Zone.
Damage Zone. - Perform the steps in Opening a Surgical Site.
- Use your
 hemostat to extract the implant. This may take several tries.
hemostat to extract the implant. This may take several tries.
- Note that there is a brief period where nothing happens after you click on the patient with the hemostat. Use this time to click on the patient multiple times to queue up multiple attempts at removing implants
- Perform the steps in Closing a Surgical Site.
Alien Embryo Removal
Removing hazardous parasites from the body.
- (Optional) Complete Prepping for Surgery.
- Aim for the chest in the
 Damage Zone.
Damage Zone. - Perform the steps in Opening a Surgical Site.
- Use the
 hemostat to remove the alien embryo.
hemostat to remove the alien embryo. - Perform the steps in Closing a Surgical Site.
Organ Removal/Transplantation
Removal and re-insertion of the brain or other organs
- (Optional) Complete Prepping for Surgery.
- Aim for the organ's location in the
 Damage Zone. (Head for brain/eyes, chest for heart/liver/lungs, groin for appendix/kidney)
Damage Zone. (Head for brain/eyes, chest for heart/liver/lungs, groin for appendix/kidney) - Perform the steps in Opening a Surgical Site.
Removing an organ:
- Use the
 scalpel. This will open up a window asking you which organ you'd like to cut loose.
scalpel. This will open up a window asking you which organ you'd like to cut loose. - Use the
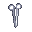 'hemostat. This will open up a window asking you which loose organ you'd like to remove.
'hemostat. This will open up a window asking you which loose organ you'd like to remove. - Dispose of the organ or store it in a freezer. For Borgification, place the brain in an
 MMI and give it to a Roboticist.
MMI and give it to a Roboticist.
Inserting an organ:
- Use the organ you intend to transplant on the patient.
- Use the
 FixOVein to reconnect the organ to the body.
FixOVein to reconnect the organ to the body. - Administer a
 advanced trauma kit or use the
advanced trauma kit or use the  nanopaste if required, to repair any damage received during transport/transplantation.
nanopaste if required, to repair any damage received during transport/transplantation. - Perform the steps in Closing a Surgical Site.
Organs may become infected after transplantation. Do not transplant organic organs that are no the patient's, otherwise they will be rejected and the patient will soon die.
Head Reattachment
Reattaching a severed head for simpler resleeving.
- Acquire the cadaver and its head.
- Aim for the cadaver's head in the
 Damage Zone.
Damage Zone. - Use a
 retractor to peel back the flesh.
retractor to peel back the flesh. - Use the
 FixOVein to shape the esophogal and vocal region.
FixOVein to shape the esophogal and vocal region. - Use a
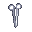 hemostat to staple and suture back the flesh.
hemostat to staple and suture back the flesh. - Use the
 cautery to adjust the area around the neck.
cautery to adjust the area around the neck. - Use the severed head to reattach it to the body.
Necrotic Limb Repair
Fixing limb necrosis caused by septic infections. Not organs.
- (Optional) Complete Prepping for Surgery.
- Aim for the necrotic organ in the
 Damage Zone.
Damage Zone. - Perform the steps in Opening a Surgical Site.
- Use the
 scalpel to cut away the dead flesh.
scalpel to cut away the dead flesh. - Use a
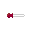 dropper filled with Peridaxon to revive the necrotic organ.
dropper filled with Peridaxon to revive the necrotic organ. - Perform the steps in Closing a Surgical Site.
Autopsy
Examination of cadavers to find cause of death. See autopsy prodedures for more information.
Hardsuit Removal
Cutting the seals on a sealed hardsuit so that it can be removed from the person wearing it.
| Guide Table | ||||||||
| Starter | VORE-Specific | Medical | Engineering | Science | Security | Other | Development | |